TLS 1.0, TLS 1.1, TLS 1.2
NOTICE! The information contained in this article is Windows Operating System-environment information. This is posted for your awareness only. If you are experiencing performance issues based on your Windows Operating System, it is your responsibility to troubleshoot and resolve the issue(s). We are here to help guide you as best we can, but please understand we cannot serve as a direct replacement for an onsite IT professional employed by your company to administrate your network.
You may have received notices from various companies saying they're stopping support for TLS 1.0.
Here's what that means: Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a security system that protects your Internet communications by preventing hackers from reading your messages. TLS 1.0 was the first version; it was effective at the time of its release. However, as hackers improved their techniques and computers became more powerful, TLS 1.0 became less secure. Consequently, newer versions, such as TLS 1.1 and 1.2, were developed to provide stronger security.
Many companies kept using TLS 1.0 because older computers can't use the newer versions. But now TLS 1.0 is too easy to hack, so most companies are stopping its use.
If you're using Windows XP or Vista, your computer won't be able to connect to these companies unless you upgrade to a newer Windows version. If you're using Windows 7 or newer, you should be fine as long as you have a recent version of TLS turned on. Windows 8 and newer usually have this on automatically. For Windows 7, you might need to turn it on yourself. Here's how to make sure it's on:
Microsoft-direct download resource
Information on this download can be found here: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/topic/update-to-enable-tls-1-1-and-tls-1-2-as-default-secure-protocols-in-winhttp-in-windows-c4bd73d2-31d7-761e-0178-11268bb10392
Clients have reported resolution for TLS issues using this download. This download from this link is a Microsoft product, and we do not design, control, or distribute this content.
https://download.microsoft.com/download/0/6/5/0658B1A7-6D2E-474F-BC2C-D69E5B9E9A68/MicrosoftEasyFix51044.msi
Manually enabling TLS
click the Windows Start button and open the Control Panel:
(If you don’t see “Control Panel” offered as per above, just type “control panel” in the search box.)
In the Control Panel, select Internet Options:
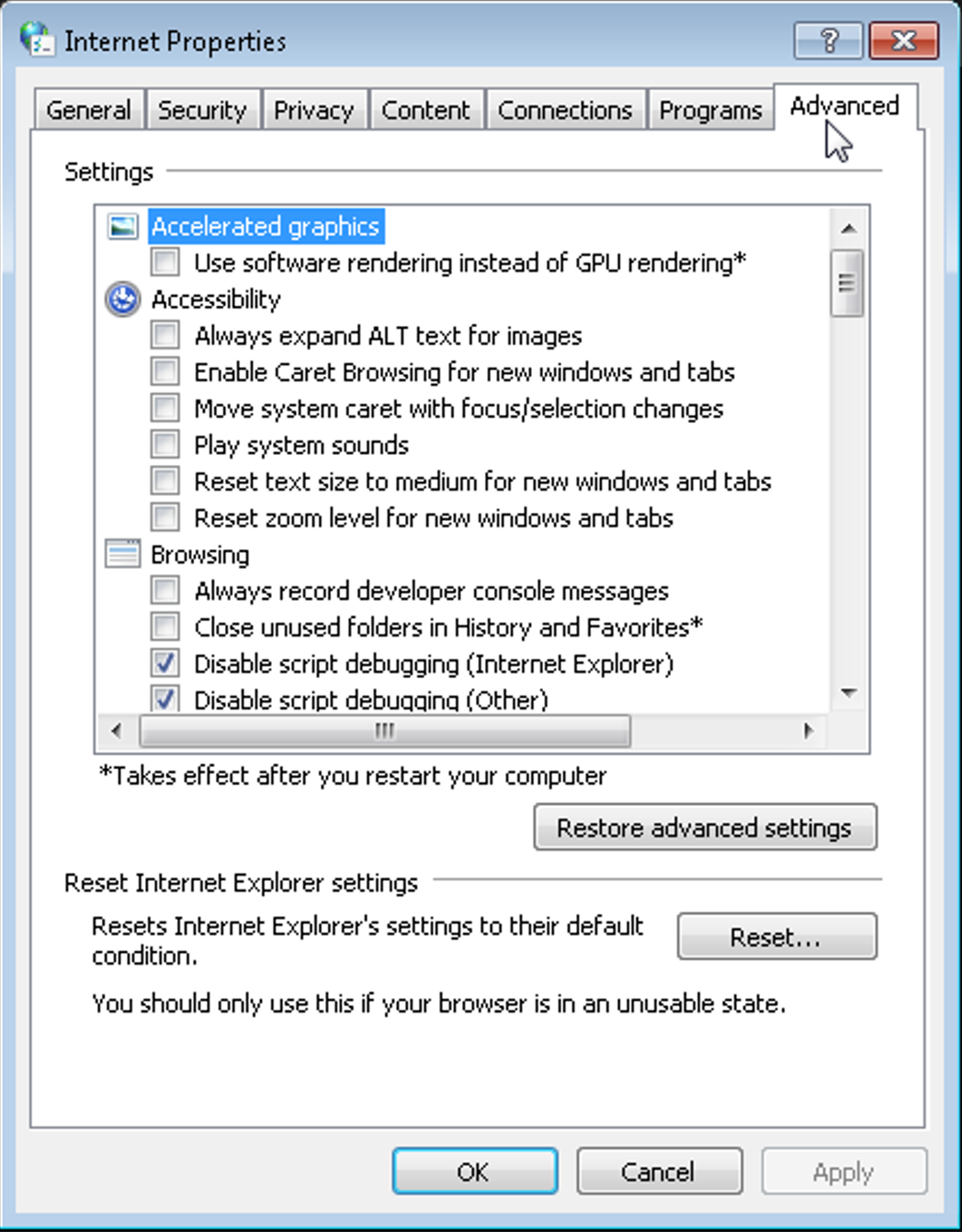
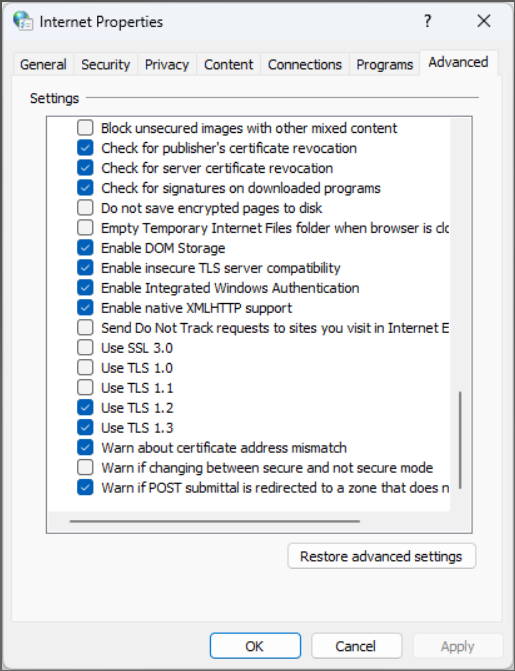
In the Internet Properties window which then appears, select the Advanced tab:
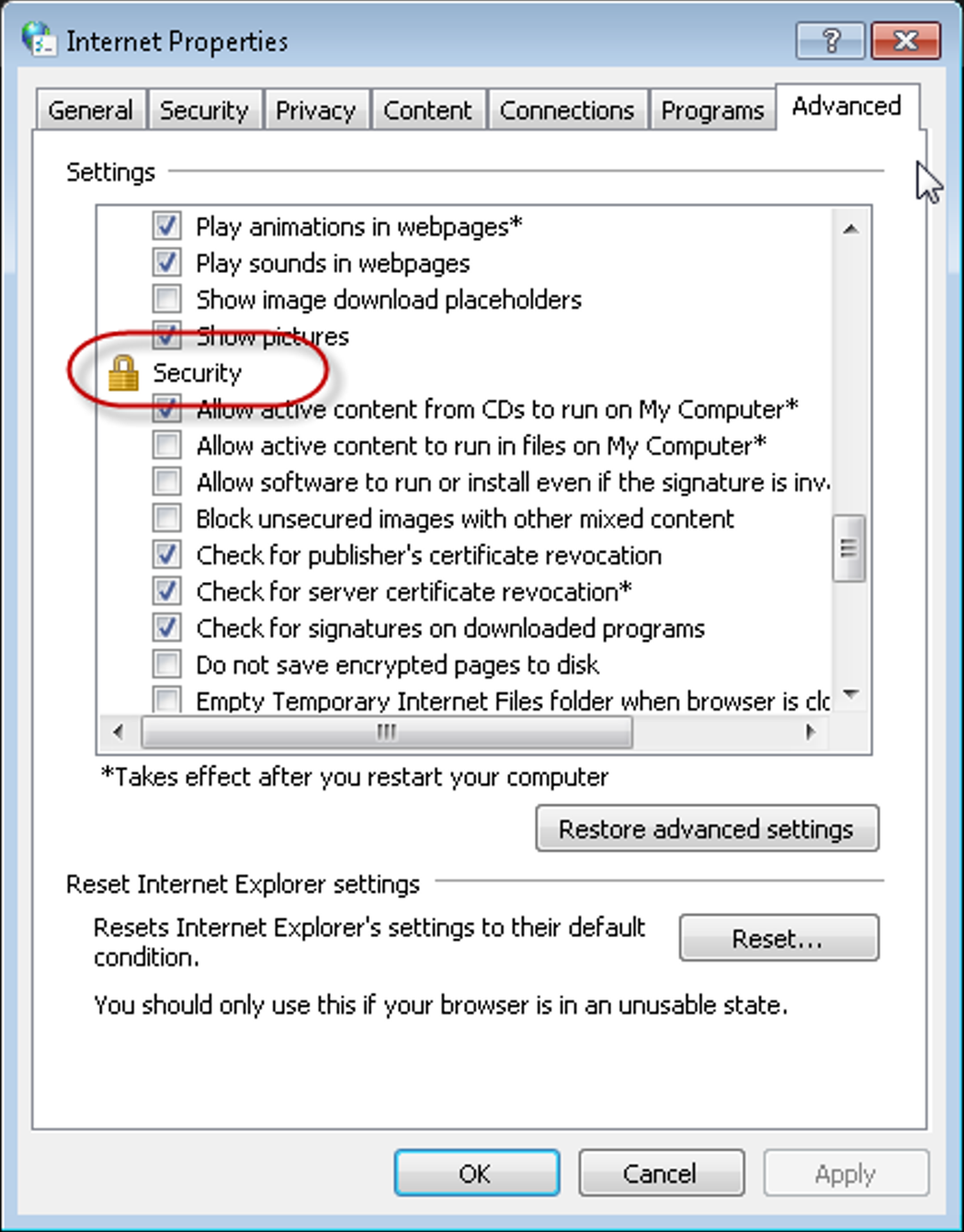
scroll down in section of settings to the section that’s labeled Security:
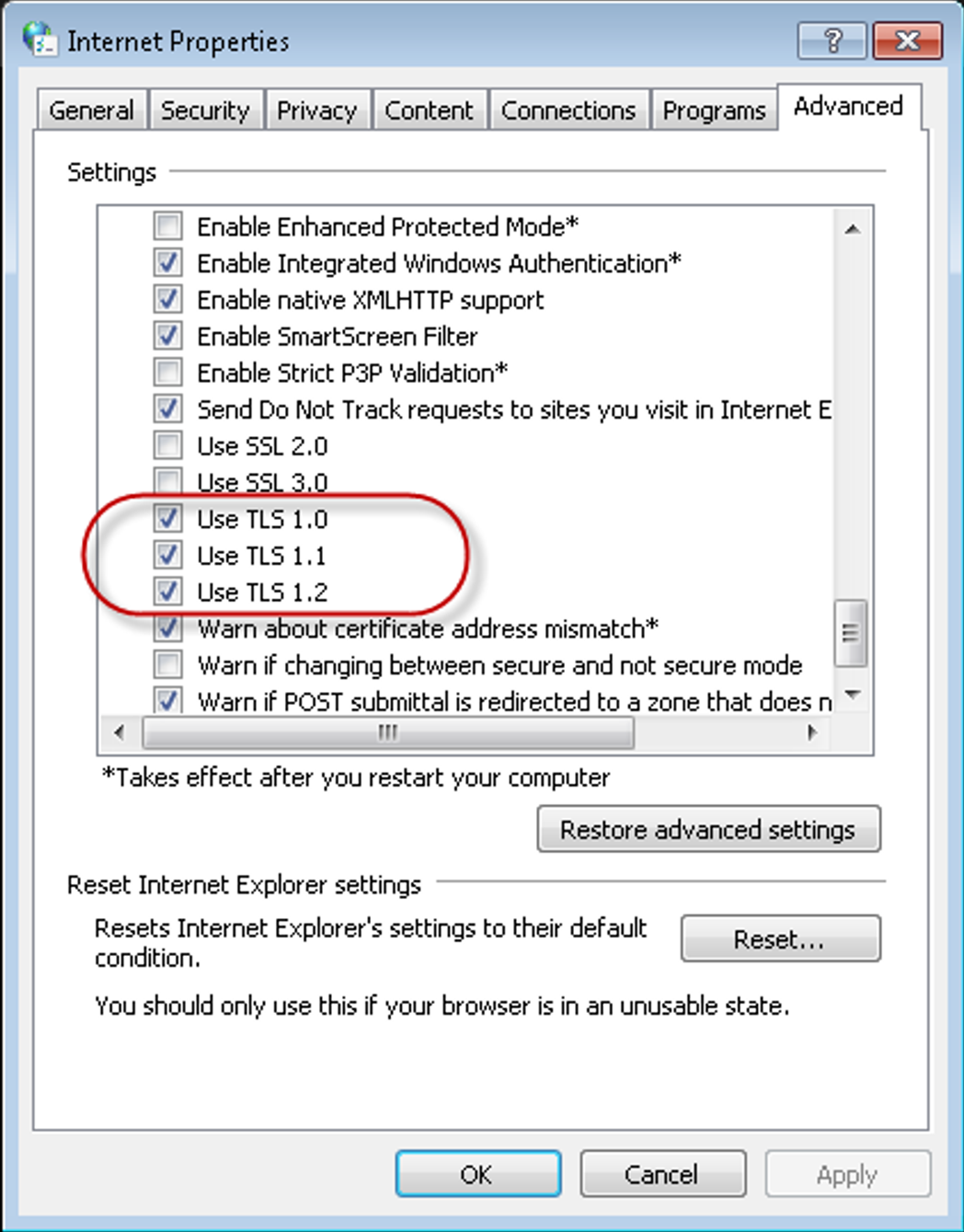
scroll further in that section to where you see check boxes for the three different versions of TLS:
Assure that all three versions are checked (as shown above). The process is complete.
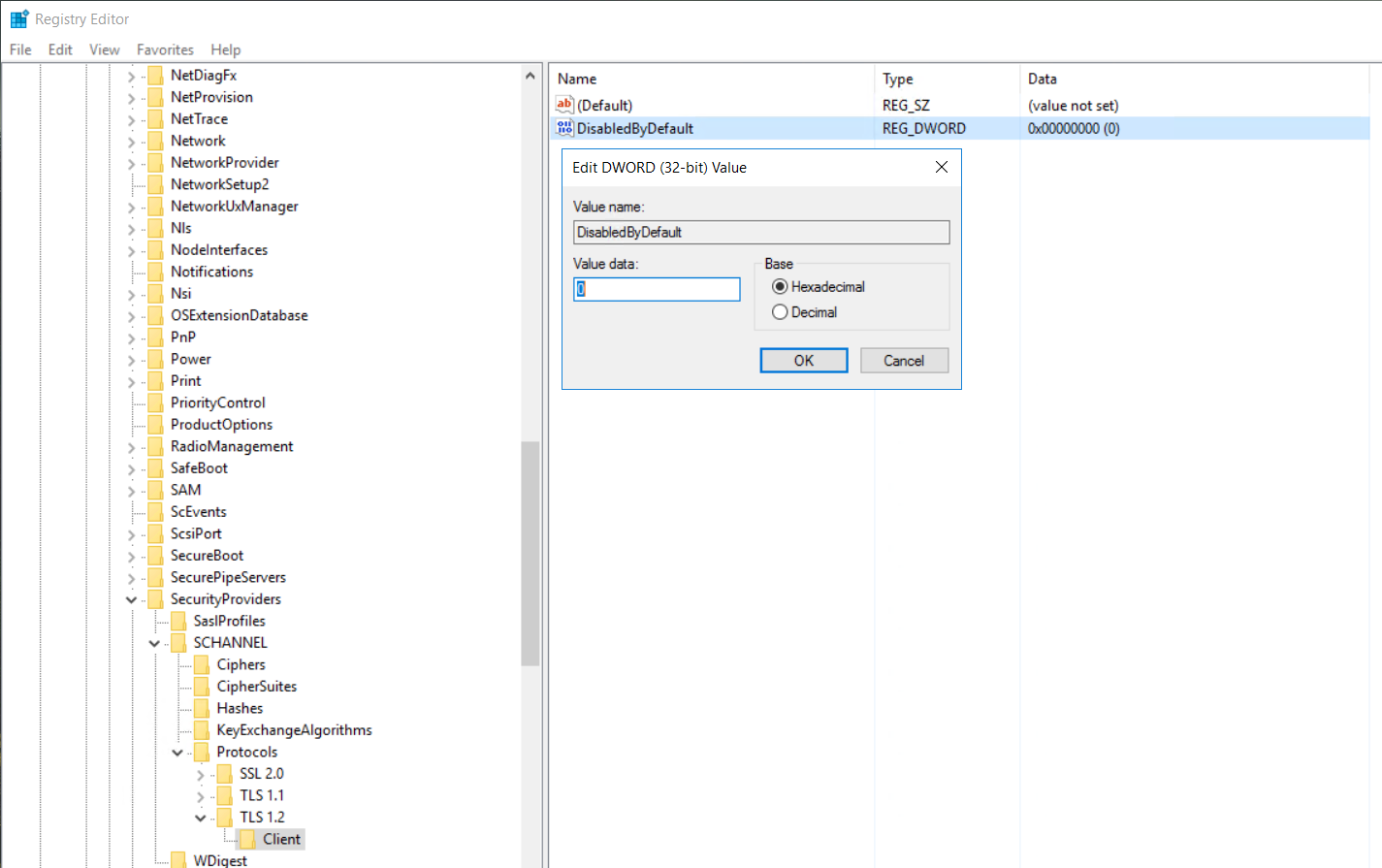
Registry setting for TLS 1.2
If you are confident in working with the Windows Registry, it might be helpful to ensure that this key is set appropriately.
For and stops hackers from reading your messages. TLS 1.0 was the first version. It was good when it was made, but as hackers improved and computers became more powerful, TLS 1.0 became less secure. So, newer versions, like TLS 1.1 and 1.2, TLS 1.2
Registry location: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client
DWORD name: DisabledByDefault
DWORD value: 0
Additional considerations
Some clients have found it necessary to uncheck the TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 to achieve resolution.